Electric vehicles (EVs) are getting more popular. This means more people want to know how to charge them at home. Charging your car at home is like charging your phone. It’s easy, saves money, and works well.
But, what do you need to think about when setting up a home charging station? Let’s explore how to charge electric cars at home.

Key Takeaways
- Electric car drivers mostly charge at home. It’s easy to do while they sleep.
- Home charging points are small, weatherproof units. They are mounted on a wall with a charging cable or socket.
- Electric cars have either a Type 1 or Type 2 connector. Make sure your home charger matches your car’s connector.
- Charging at home is cheap and convenient. It keeps your electric vehicle ready to go.
- More charging spots are showing up at work and in public. This is good news for electric car owners.
Understanding Home EV Charging Basics
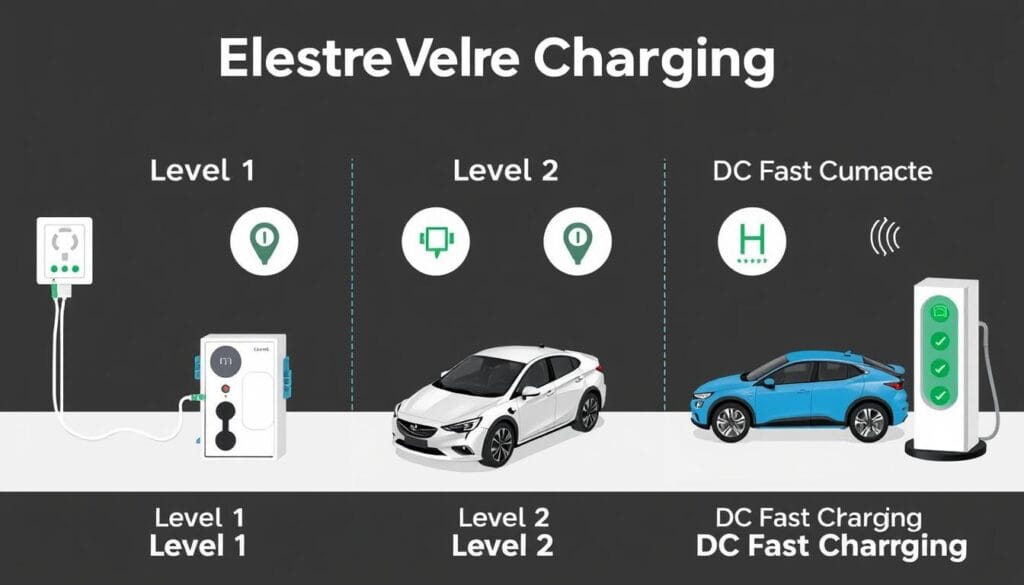
Charging your electric vehicle (EV) at home is easy once you know the basics. There are two main types of home chargers: Level 1 and Level 2. Each has its own benefits.
Types of Home Charging Equipment
Level 1 chargers use a standard 120-volt outlet. This is great for many EV owners. Most new EVs come with a charger for these outlets.
Level 2 chargers need a 240-volt outlet, like for big appliances. They charge faster than Level 1 chargers.
Essential Components for Home Charging
You need a charging unit, the right connectors, and proper electrical setup for home charging. Make sure the equipment is safe and meets local codes. A certified professional should install it.
Safety Considerations for Home Setup
Safety is key when setting up a home EV charging station. Outdoor units must be weatherproof. The system must follow local electrical codes.
Grounding and surge protection are also vital. They keep the charger and your home safe.
| Charging Level | Voltage | Charging Speed | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 120V AC | 3-5 miles of range per hour of charging | Overnight charging at home |
| Level 2 | 240V AC | 10-20 miles of range per hour of charging | Faster charging at home or public charging stations |
Learning about home EV charging helps you set up a safe and efficient system. With the right gear and installation, charging at home is easy. This reduces your need for public charging and makes driving electric better.
How to Charge Electric Cars at Home
Charging your electric car at home is easy and saves money. You can install a home charging station. This makes sure your car is always ready to go.
To charge your car at home, you need a home charging point. You can use a simple plug or a more advanced Level 2 station. Most people charge their cars overnight or when they’re parked at home.
Home charging lets you set a top charge limit. This keeps your battery healthy. Also, some energy providers offer cheaper rates at night. This can help you save on electricity costs.
| Charging Level | Charging Speed | Typical Range Added per Hour |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (120V) | 1.8 kW | 4-5 miles |
| Level 2 (240V) | 3.6 kW to 12 kW | 25-30 miles |
| DC Fast Charging | 50 kW to 350 kW | Up to 250 miles |
The NISSAN ENERGY Charge network gives Nissan ARIYA owners access to over 90,000 public chargers. You can use the MyNISSAN App to find them. With the right home charger, your car will always be ready to go.

Different Charging Levels Explained
As electric vehicles (EVs) become more popular, knowing about ev charging levels is key. These levels affect how fast and well your car’s battery is charged. They range from using a standard outlet to high-power stations.
Level 1 Charging: Standard Household Outlet
Level 1 electric car charging cables use a 120-volt AC outlet. They give 1 kW to 1.8 kW of power. It takes 22-40 hours to fully charge a car, adding 3-7 miles per hour.
Level 2 Charging: Dedicated Home Station
Level 2 electric vehicle charging guide uses a 240-volt AC outlet. It offers 3 kW to 22 kW of power. This can give 10-75 miles per hour, charging a 40 kWh battery in 2-13 hours.
Comparing Charging Speeds and Efficiency
Level 1 charging is good for occasional use. But Level 2 is faster and better for daily ev charging levels at home. Level 3 (DC fast charging) stations can charge a car in under 20 minutes. They offer 120 – 1400+ miles per hour of charging.
Choosing a charging level depends on your needs and your car’s capabilities. It also depends on the charging options in your area. Knowing the pros and cons of each level helps you choose the best electric car charging cables for your needs.
Home EV Charger Installation Process
Installing a home electric vehicle (EV) charger is key for EV owners. It lets them charge their cars at home. The charger goes on an outside wall or in the garage. The whole job might take about three hours.
It’s best to get certified pros to do the job. They make sure it’s safe and follows local rules. They connect the charger to your home’s power and might need to upgrade your electrical panel.
It’s good for the homeowner to be there during the install. They can help pick the best spot for the charger. They also learn how to use it well.
Key Steps in the Installation Process
- Check your home’s electrical setup to see if upgrades are needed.
- Find the best spot for the charger, thinking about where it’s easy to get to and looks good.
- Put the charger up on the wall or in the garage, making sure it’s straight and level.
- Hook up the charger to your home’s power, usually by adding a special circuit.
- Make sure the charger works right and is safe to use.
- Teach the homeowner how to use the charger and its special features.
By following these steps and hiring certified pros, you can get your charger installed safely and quickly. This makes driving electric easy and smooth.

Cost Considerations for Home EV Charging
Switching to an electric vehicle (EV) has many benefits. But, the costs of charging at home are key to understand. From the setup costs to the daily expenses, it affects your driving experience a lot.
Installation Expenses
Getting a home charging station can cost between less than $1,000 and over $3,000. This includes the charger, labor, and any needed electrical work. But, you can get help with these costs through tax credits and rebates.
Operational Costs and Electricity Rates
Charging your EV at home is cheaper than gas cars. The U.S. average electricity cost is $0.16 per kilowatt-hour. This means a full charge costs about $6.00 to $6.40 for a 40 kWh battery. Costs can change based on your area’s rates and rebates, like off-peak hours.
| Charging Level | Charging Time | Cost per Charge (40 kWh battery) |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 (Household Outlet) | 12-24 hours | $6.40 |
| Level 2 (Dedicated Home Station) | 3-8 hours | $6.00 |
| Public Fast DC Charging | 15-45 minutes | $16.00 – $24.00 |
Charging at home can save you about $950 a year compared to gas cars. Over time, you could save $6,000 to $10,000.
Available Tax Incentives and Rebates
Many governments and utility companies offer incentives for EVs and home charging. You can get up to $7,500 in federal tax credits. Plus, there are state, local, and utility rebates to help with the costs.

Smart Charging Features and Benefits
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular. This means smart EV charging solutions are getting more important. Smart home chargers help EV owners save money and charge more efficiently.
One big plus of smart EV charging is power balancing. These chargers adjust the charge rate to avoid overloading the home’s electrical supply. This ensures charging goes smoothly, even when other appliances are using a lot of power.
Smart EV chargers can also charge during off-peak hours. This helps save money because electricity rates are lower then. Some chargers even let you control charging from your phone, making it easy to manage your energy use.
Smart EV charging
Smart EV charging also helps with using energy in a green way. These chargers work with home energy systems. This lets drivers use their own renewable energy to charge their EVs, making energy use more flexible and sustainable.
In the future, smart EV charging might support sending power back to the grid or home. This could make energy use even more flexible and resilient. It would be good for both the EV owner and the electricity network.
As electric vehicles become more common, smart EV charging will be key. It will help EV owners, fleet operators, and utilities. By using these smart technologies, EV drivers can charge more efficiently, saving money and using energy in a sustainable way.
| Smart EV Charging Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Power Balancing | Prevents overloading the home’s electrical supply, ensuring uninterrupted charging |
| Off-Peak Charging Scheduling | Reduces operational costs by taking advantage of lower electricity rates |
| Remote Monitoring and Control | Allows users to manage charging schedule and energy consumption on the go |
| Integration with Home Energy Management Systems | Enhances energy flexibility and utilization for households with renewable energy generation |
| Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) and Vehicle-to-Home (V2H) Support | Improves energy flexibility and resilience by allowing EV batteries to provide power back to the grid or a household |

“Smart charging can lead to cost savings over the charger’s lifespan by providing insights into charging processes, enabling users to manage electricity consumption efficiently, and charge at times with lower electricity rates.”
Optimizing Your Home Charging Setup
As an electric vehicle (EV) owner, making your home charging better can save you money. By following best practices and using smart charging, you get the most out of your setup. This includes your ev home charging station and residential ev chargers.
Best Practices for Efficient Charging
Charge your EV when electricity is cheap, like off-peak hours. Many EVs and smart chargers let you set charging times. This way, your car charges when power is less expensive.
Managing Energy Load and Consumption
Using smart charging tech with your ev home charging station helps control energy use. Features like Auto Power Balancing adjust the charge rate. This prevents your home’s power from getting overloaded.
Time-of-Use Rate Optimization
Some places have time-of-use (TOU) rates for electricity. The cost changes with the time of day. Charging your EV when it’s cheaper can cut down your costs a lot. Watching your energy use and adjusting your charging can save you even more.
Adding solar powered ev charging to your setup is also smart. It uses your own solar energy. This can make your charging costs almost zero or very low.
“Smart charging features and strategic scheduling can help you maximize the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of your home EV charging setup.”
Common Charging Connectors and Compatibility
Charging your electric car at home or on the go needs you to know about different connectors. In North America, you’ll find J1772, CCS, CHAdeMO, and Tesla’s special connector.
The J1772 connector is common for Level 1 and Level 2 charging. It can give up to 19.2 kW of power. CCS connectors are great for DC fast charging, with up to 360 kW power. CHAdeMO connectors, used by Nissan, can charge up to 400 kW.
Tesla cars have their own connector, but you can use adapters for other standards. Knowing your car’s connector is key for using electric car charging cables and ev charging station systems.
| Connector Type | Maximum Power Output | Charging Speed |
|---|---|---|
| J1772 (Type 1) | 19.2 kW | Level 1 and Level 2 |
| CCS (Type 1 and Type 2) | 360 kW | DC Fast Charging |
| CHAdeMO | 400 kW | DC Fast Charging |
| Tesla Proprietary | Varies | Level 1, Level 2, and Supercharging |
It’s important to know the right electric car charging cables and ev charging station for your car. This ensures a smooth charging experience, whether at home or on the move.
Tips for Apartment and Condo Dwellers
Start by checking if your building has EV charging. Many places are adding charging units in parking garages. Talk to your property manager to see if you can get a charger or use shared ones.
If there’s no charging yet, a portable Level 1 charger might help. It plugs into your home outlet. But, it takes longer to charge. Also, look for public charging spots nearby or see if your work has EV charging.
As more people want EV charging, ask for better options in your area. Work with your landlord or local government to get ev charging for apartments and residential ev charging solutions. This will help all EV owners in your building.
FAQ
What is the process for charging an electric car at home?
To charge an electric car at home, first install a charging point near where you park. Plug the cable into your car and the charger. For quick charges, use a 3-pin plug.
Charging can happen overnight or when your car is parked at home.
What are the different levels of home charging for electric cars?
There are two main levels of home charging:
Level 1 uses a standard 120V outlet and gives 2-5 miles per hour but Level 2 uses a 240V outlet and gives 10-60 miles per hour. Level 2 is faster and more efficient.
What is involved in installing a home charging station?
Installing a home charger takes about three hours. It involves mounting the unit on a wall or in a garage. You’ll need to connect it to your home’s electrical supply.
Upgrades to your electrical panel might be needed. Always have certified professionals do the installation for safety and to follow local rules.
How much does it cost to charge an electric car at home?
Costs for home EV charging include installation and operational costs. Installation starts at $849. Operational costs depend on your local electricity rates.
Electricity rates vary, but some tariffs offer cheaper rates. Many areas also offer tax incentives and rebates to help with costs.
What are the benefits of smart home charging features?
Smart home chargers offer power balancing to avoid overloading your electrical supply. They can charge during off-peak hours for savings. Some chargers let you monitor and control charging remotely.
What are the common charging connectors for electric cars?
The most common connectors include J1772, CCS, CHAdeMO, and Tesla’s connector. Knowing your car’s connector type is key for using public charging stations.
How can apartment and condo dwellers charge their electric cars at home?
If you live in an apartment or condo, check if your building has EV charging. If not, talk to management about installing a charger. Portable Level 1 chargers work with standard outlets if you can’t install a dedicated charger.
Using nearby public charging stations is another option.
Source Links
- Charging Your Vehicle – Electric For All – https://www.electricforall.org/how-can-i-fill-up/charging-your-vehicle/
- Charging an Electric Car at Home | Pod Point – https://pod-point.com/guides/driver/charging-electric-car-at-home?srsltid=AfmBOopw5F3YXYZpLQqrwxfvqpj0vCM4ct1diC1TCVVed2AOTWFluztG
- Charging Electric Vehicles at Home – https://afdc.energy.gov/fuels/electricity-charging-home
- EV 101: Electric Vehicle Charging Guide | About EVs and How to Charge – https://www.evgo.com/ev-drivers/charging-basics/
- How To Charge an Electric Car | Nissan USA – https://www.nissanusa.com/experience-nissan/news-and-events/how-to-charge-electric-car.html
- How to charge your electric car at home – https://www.tomsguide.com/how-to/how-to-charge-your-electric-car-at-home
- How Do You Charge an Electric Car at Home? | Mercury Insurance – https://www.mercuryinsurance.com/resources/electric-vehicles/can-you-charge-an-electric-car-at-home-without-a-garage.html
- The Different Levels of EV Charging Explained – EVESCO – https://www.power-sonic.com/blog/levels-of-ev-charging/
- EV charging levels explained [2023 update] | EVBox – https://blog.evbox.com/ev-charging-levels
- How to Prepare Your Home and Garage for an Electric Vehicle – https://www.thespruce.com/installing-electric-car-charger-at-home-6504202
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging – https://www.pge.com/en/clean-energy/electric-vehicles/getting-started-with-electric-vehicles/electric-vehicle-charging.html
- Electric Vehicles (EV) – https://www.sce.com/residential/ev-charging
- Cost Analysis of EV Home Charging vs. Public Charging | Qmerit – https://qmerit.com/blog/comparing-long-term-cost-analysis-of-ev-home-charging-vs-public-charging/
- Discover the Cost Savings of Electric Vehicle Home Charging – https://energyharbor.com/en/energy-resources/energy-savings-tips/how-to-save-on-at-home-electric-vehicle-charging-costs
- Smart EV Charging: Your Essential Energy Management Guide – https://driivz.com/blog/ev-smart-charging-benefits/
- The 5 top benefits of EV smart charging at home | EVBox – https://blog.evbox.com/5-benefits-smart-charging
- No title found – https://evbox.com/en/smart-charging
- EV Charging Guide: How to Charge Your Electric Vehicle at Home? – https://store.autelenergy.com/blogs/blog/how-to-charge-your-electric-vehicle-at-home?srsltid=AfmBOoqou8WVFB4WgBgNTW6-3DTdpHVmSa7LUJQYPYE0qt-CwQEKzjjj
- How to optimize home charging to save time and money – Futurehome – https://www.futurehome.io/en_no/how-to-optimize-home-charging-to-save-time-and-money?srsltid=AfmBOopQub8CGxYcwOG1B82PhBc3Y7WHLGEqiw6PkC0HrTcvmciYmyUe
- Charging an Electric Car at Home | Pod Point – https://pod-point.com/guides/driver/charging-electric-car-at-home?srsltid=AfmBOorfxiB3l4YT4W-HM35oACaF2kx3DDPGYwWj6EsMuBmg9lseGGVH
- EV Charging Connector Types: A Complete Guide – EVESCO – https://www.power-sonic.com/blog/ev-charging-connector-types/
- How To Charge Electric Vehicles – https://www.energy.gov/energysaver/how-charge-electric-vehicles
- 5 EV charging tips for apartments and condos – https://witricity.com/media/blog/5-ev-charging-tips-for-builders-and-managers-of-apartments-and-condos
- Apartment EV Charging: Methods, Costs, & 3 Best Solutions – https://butterflymx.com/blog/apartment-ev-charging/
- How to Charge an Electric Car In Apartment Buildings – Cyberswitching – https://cyberswitching.com/electric-vehicle-charging-in-apartment-buildings/?srsltid=AfmBOoqQCwKmPffYsDYZcevM6hp4PZL1ksdhMkBECMly8pOpqdAeg4Wb

1 thought on “How to Charge Electric Cars at Home – EV Charging Guide”